Chicken Breast Nutrition Facts: Detailed
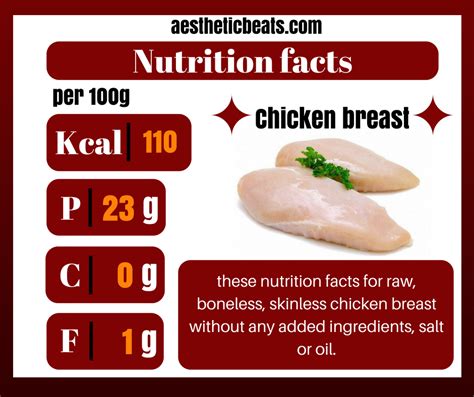
Chicken breast is one of the most popular and versatile cuts of poultry, renowned for its lean protein content and numerous health benefits. When it comes to nutrition, chicken breast stands out due to its high protein and low fat composition, making it a staple in many diets, especially for those focusing on weight management and muscle building. To delve into the specifics of chicken breast nutrition, it's essential to examine the detailed breakdown of its nutritional components.
Nutritional Overview of Chicken Breast

A 3-ounce serving of cooked chicken breast, which is about the size of a deck of cards, contains approximately 26 grams of protein, 3.6 grams of fat, and zero carbohydrates. This same serving size provides a significant amount of essential vitamins and minerals, including niacin, vitamin B6, and selenium. The low fat content, coupled with its high protein level, makes chicken breast an attractive choice for health-conscious consumers. Furthermore, chicken breast is rich in antioxidants and other beneficial compounds that can help protect against cell damage and reduce inflammation in the body.
Macronutrient Breakdown
The macronutrient composition of chicken breast is characterized by its high protein and low fat content. On average, a cooked chicken breast contains:
- Protein: 31 grams per 3-ounce serving, contributing to muscle growth and repair.
- Fat: 3.6 grams per 3-ounce serving, with less than 1 gram being saturated fat, making it a heart-healthy option.
- Carbohydrates: 0 grams, which is particularly beneficial for individuals following low-carb diets.
This balance of macronutrients supports a variety of dietary needs and preferences, from low-carb and keto diets to high-protein meal plans aimed at athletes and bodybuilders.
Micronutrient Content
Beyond its macronutrient profile, chicken breast is also a rich source of several micronutrients that are crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing disease. Key micronutrients found in chicken breast include:
| Micronutrient | Amount per 3-ounce serving |
|---|---|
| Niacin | 59.1 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.5 mg |
| Selenium | 24.3 mcg |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.3 mcg |
| Phosphorus | 165 mg |

These vitamins and minerals play vital roles in energy production, nerve function, immune system operation, and the formation of red blood cells, among other physiological processes.
Health Benefits of Consuming Chicken Breast

The consumption of chicken breast has been associated with several health benefits, largely due to its nutrient-dense profile. Weight Management: The high protein and low fat content in chicken breast make it an excellent choice for those looking to lose weight or maintain weight loss. Muscle Growth and Repair: The protein in chicken breast is rich in essential amino acids, which are vital for building and repairing muscle tissue. Heart Health: Chicken breast is low in saturated fats and high in nutrients like niacin and vitamin B6, which can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Dietary Considerations and Preparations
Chicken breast can be incorporated into a wide range of diets and can be prepared in numerous ways to enhance its flavor and nutritional value. Some popular preparation methods include grilling, baking, sautéing, and stir-frying. When preparing chicken breast, it’s essential to cook it to an internal temperature of at least 165°F (74°C) to ensure food safety. Additionally, marinating chicken breast before cooking can not only add flavor but also help retain moisture and reduce the formation of potentially harmful compounds during high-heat cooking.
Is chicken breast a good source of iron?
+Chicken breast contains a small amount of iron, approximately 0.5 mg per 3-ounce serving. While it is not as rich in iron as red meat or fortified cereals, it can still contribute to daily iron intake, especially when consumed as part of a balanced diet.
Can chicken breast help with muscle recovery after exercise?
+Yes, chicken breast can be beneficial for muscle recovery due to its high protein content. Consuming protein after exercise can help promote muscle protein synthesis, which is crucial for repairing and building muscle tissue.
In conclusion, chicken breast is a nutrient-rich food that offers a multitude of health benefits, from supporting weight management and muscle growth to contributing to heart health. Its versatility in cooking and preparation, combined with its favorable nutritional profile, make it a valuable addition to a balanced diet. Whether you’re an athlete, a health enthusiast, or simply looking to incorporate more protein into your meals, chicken breast is a worthwhile consideration.

