What Are Chicken's Nutritional Benefits? A 100G Breakdown

Chicken, a versatile and widely consumed protein source, offers a plethora of nutritional benefits that contribute to a healthy diet. Understanding the nutritional breakdown of chicken can help individuals make informed choices about their food intake and appreciate the value this popular meat brings to the table.
Nutritional Profile of Chicken: A Comprehensive Overview
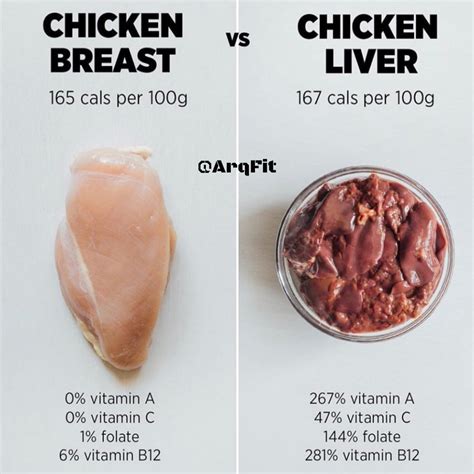
Chicken, specifically the breast meat without skin, is renowned for its high protein content. A 100-gram serving of cooked chicken breast boasts approximately 31 grams of protein, making it an excellent choice for those seeking to increase their protein intake. This lean protein source also contains minimal fat, with only 3 grams of fat per 100 grams, making it a popular choice for health-conscious individuals.
In addition to its protein content, chicken provides a range of essential vitamins and minerals. It is a good source of vitamin B6, with a 100-gram serving providing around 40% of the recommended daily intake. Vitamin B6 is crucial for brain development and function, as well as for the production of neurotransmitters and hormones.
Chicken also contains vitamin B12, a nutrient essential for maintaining healthy nerve cells and red blood cells. A 100-gram serving of chicken offers around 15% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin B12, making it a valuable dietary source for individuals at risk of deficiency.
Furthermore, chicken is rich in selenium, an essential mineral with powerful antioxidant properties. Selenium plays a vital role in protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals and is believed to have cancer-preventative effects. A 100-gram serving of chicken provides approximately 30% of the recommended daily intake of selenium, highlighting its importance in a balanced diet.
While chicken is a great source of protein and essential nutrients, it is important to note that its nutritional profile can vary depending on the cut of meat and cooking method. For instance, dark meat chicken, such as thigh or drumstick, contains slightly more fat and calories compared to breast meat. Additionally, frying or deep-frying chicken can significantly increase its fat content, whereas grilling or baking can help retain its nutritional value.
Nutritional Breakdown of Chicken: A Detailed Examination
When examining the nutritional breakdown of chicken, it is essential to consider its macronutrient composition. As mentioned, chicken is an excellent source of high-quality protein, which is essential for muscle growth and repair, enzyme and hormone production, and maintaining a healthy immune system.
In addition to protein, chicken also contains a small amount of carbohydrates. A 100-gram serving of chicken breast provides less than 1 gram of carbohydrates, making it a suitable choice for individuals following low-carbohydrate diets. This minimal carbohydrate content also makes chicken an ideal food for those with diabetes, as it has a negligible impact on blood sugar levels.
The fat content of chicken, while relatively low, is also worth noting. While chicken breast is typically lean, other cuts such as thighs or legs may contain more fat, particularly if the skin is left on. However, even with the skin, the fat content of chicken is still considered moderate compared to other animal proteins. It is important to choose leaner cuts of chicken and remove the skin to minimize fat intake.
Chicken also contains a range of micronutrients, including iron, zinc, and magnesium. Iron is essential for the production of red blood cells and the transportation of oxygen throughout the body. Zinc plays a crucial role in immune function, wound healing, and DNA synthesis. Magnesium, on the other hand, is involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, including muscle and nerve function, blood glucose control, and blood pressure regulation.
| Nutrient | Amount (100g) |
|---|---|
| Protein | 31g |
| Fat | 3g |
| Vitamin B6 | 40% RDI |
| Vitamin B12 | 15% RDI |
| Selenium | 30% RDI |
| Carbohydrates | <1g |
| Iron | Variable |
| Zinc | Variable |
| Magnesium | Variable |
The Role of Chicken in a Healthy Diet: Practical Tips and Recommendations

Incorporating chicken into a balanced diet can offer numerous health benefits. Its high protein content can aid in weight management by promoting feelings of fullness and supporting muscle maintenance during weight loss. Additionally, the vitamins and minerals found in chicken can contribute to overall health and well-being.
To maximize the nutritional benefits of chicken, it is recommended to choose lean cuts and prepare them using healthy cooking methods. Baking, grilling, or poaching are excellent choices as they do not require added fats and help retain the natural flavors of the meat. If using oil for cooking, opt for healthier options like olive oil or avocado oil.
For those looking to reduce their carbohydrate intake, chicken can be a valuable addition to their diet. Its minimal carbohydrate content makes it a suitable choice for individuals following low-carbohydrate or ketogenic diets. Combining chicken with a variety of non-starchy vegetables can create a nutritious and satisfying meal.
Furthermore, chicken can be a versatile ingredient in various dishes, allowing for creativity in the kitchen. It can be used in salads, soups, stir-fries, curries, and even as a main course. Experimenting with different herbs, spices, and marinades can add flavor and variety to chicken dishes, making them both delicious and nutritious.
It is also important to consider the overall balance of a meal when incorporating chicken. Pairing chicken with complex carbohydrates like whole grains or legumes, and a variety of colorful vegetables, can create a well-rounded and nutritious meal. This combination provides a balance of protein, carbohydrates, and essential nutrients, supporting overall health and energy levels.
Conclusion: Embracing the Nutritional Benefits of Chicken
Chicken is a nutritional powerhouse, offering a range of benefits that contribute to a healthy diet. Its high protein content, coupled with essential vitamins and minerals, makes it an excellent choice for individuals seeking to maintain a balanced and nutritious lifestyle. By understanding the nutritional breakdown of chicken and incorporating it into a varied diet, individuals can harness its full potential for optimal health.
How does the nutritional content of chicken compare to other protein sources?
+Chicken compares favorably to other protein sources in terms of nutritional content. While red meat like beef and lamb can offer higher levels of certain nutrients, they also tend to be higher in fat and calories. Fish, on the other hand, is an excellent source of healthy omega-3 fatty acids but may not provide the same level of protein as chicken. Poultry, including chicken and turkey, generally offers a good balance of protein, vitamins, and minerals with relatively low fat content, making it a popular choice for health-conscious individuals.
Can chicken be part of a vegetarian or vegan diet?
+No, chicken is not suitable for vegetarian or vegan diets as it is an animal-based protein source. Vegetarians and vegans typically rely on plant-based protein sources such as beans, lentils, tofu, and tempeh. However, for those following a vegetarian diet, eggs and dairy products can also be valuable sources of protein and other nutrients.
What are some healthy cooking methods for chicken?
+There are several healthy cooking methods for chicken. Grilling, baking, and poaching are excellent choices as they do not require added fats and help retain the natural flavors of the meat. Stir-frying or sautéing chicken in a small amount of healthy oil, such as olive oil or avocado oil, can also be a good option. It is important to avoid deep-frying or using excessive amounts of oil, as this can significantly increase the fat content of the dish.