The Ultimate Guide To Strawberry Nutrition

Strawberries, with their vibrant red color and sweet, juicy flesh, are not only a delight to the taste buds but also a nutritional powerhouse. These small, heart-shaped fruits pack a punch when it comes to essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the nutritional profile of strawberries, exploring their health benefits, unique properties, and how they can be incorporated into a balanced diet.
The Nutritional Profile of Strawberries
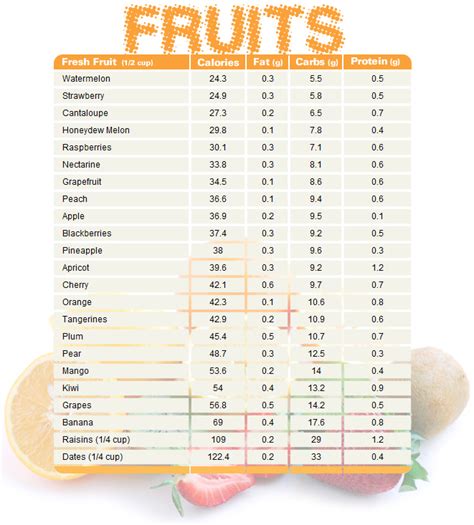
Strawberries, scientifically known as Fragaria x ananassa, are a hybrid species belonging to the Rosaceae family. Native to Europe and North America, strawberries have become a beloved fruit worldwide due to their exceptional taste and health benefits. Let’s take a closer look at the nutritional composition of these tiny red gems.
Vitamins and Minerals
Strawberries are an excellent source of essential vitamins and minerals, making them a valuable addition to any diet. Here’s a breakdown of the key nutrients found in strawberries:
- Vitamin C: Strawberries are renowned for their high vitamin C content. A single cup of strawberries provides a whopping 84.7 mg of vitamin C, which is more than the recommended daily intake for adults. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that supports immune function, collagen production, and iron absorption.
- Manganese: This essential mineral is abundant in strawberries. Manganese plays a crucial role in bone health, metabolism, and the body’s antioxidant defense system.
- Folate: Also known as vitamin B9, folate is vital for cell growth and development. Strawberries are a good source of folate, making them particularly beneficial for pregnant women and those with increased folate requirements.
- Potassium: A cup of strawberries contains a decent amount of potassium, an electrolyte that helps regulate blood pressure and maintain proper heart function.
- Vitamin B6: Vitamin B6, or pyridoxine, is essential for brain development and function. Strawberries provide a small but significant amount of this vital vitamin.
Antioxidants and Phytochemicals
One of the standout features of strawberries is their impressive antioxidant content. Antioxidants are compounds that protect our cells from damage caused by free radicals, which are unstable molecules produced as a byproduct of normal metabolic processes. Here’s a glimpse at the antioxidant power of strawberries:
- Anthocyanins: These vibrant pigments give strawberries their characteristic red color. Anthocyanins are powerful antioxidants with potential anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties.
- Ellagic Acid: Strawberries contain ellagic acid, a phytochemical with antioxidant and anti-cancer properties. It has been studied for its potential to inhibit the growth of certain cancer cells.
- Flavonols: Flavonols are a group of antioxidants found in strawberries. Quercetin and kaempferol are two prominent flavonols with anti-inflammatory and cardiovascular benefits.
- Vitamin E: While strawberries are not a rich source of vitamin E, they do contain small amounts of this essential antioxidant vitamin.
Fiber and Carbohydrates
Strawberries are a good source of dietary fiber, with approximately 2 grams of fiber per cup. Fiber is essential for digestive health, helping to regulate bowel movements and promote a healthy gut microbiome. In addition to fiber, strawberries contain primarily simple carbohydrates, with a low glycemic index, making them a suitable choice for individuals with diabetes or those watching their blood sugar levels.
Calories and Macronutrients
Despite their sweet taste, strawberries are relatively low in calories. A cup of strawberries contains only 53 calories, making them an excellent choice for those watching their calorie intake. Strawberries are naturally low in fat and protein, with trace amounts of both. However, their low-calorie content and high nutrient density make them an ideal snack or ingredient in various dishes.
Health Benefits of Strawberries

The nutritional profile of strawberries translates into a range of health benefits. Let’s explore some of the ways in which incorporating strawberries into your diet can positively impact your well-being.
Boosting Heart Health
The antioxidants and phytochemicals in strawberries have been linked to improved heart health. Regular consumption of strawberries may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease by lowering cholesterol levels, improving blood pressure, and reducing inflammation. The high potassium content in strawberries also contributes to heart health by regulating heart function.
Supporting Brain Function
Strawberries are rich in flavonoids, particularly anthocyanins, which have been associated with improved cognitive function and reduced risk of age-related cognitive decline. Studies suggest that the antioxidants in strawberries may help protect brain cells from damage and improve memory and learning.
Managing Diabetes
Due to their low glycemic index and high fiber content, strawberries can be a valuable addition to a diabetic diet. The natural sugars in strawberries are slowly released into the bloodstream, helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Additionally, the fiber in strawberries can promote a feeling of fullness, reducing the risk of overeating and aiding in weight management.
Promoting Skin Health
The high vitamin C content in strawberries contributes to collagen production, which is essential for maintaining healthy skin. Vitamin C also acts as an antioxidant, protecting the skin from damage caused by environmental factors such as pollution and UV radiation. Furthermore, the ellagic acid in strawberries has been studied for its potential to reduce skin inflammation and protect against UV-induced skin damage.
Boosting Immunity
Strawberries are an excellent source of vitamin C, which is crucial for a healthy immune system. Vitamin C helps stimulate the production of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting off infections and illnesses. Additionally, the antioxidants in strawberries can help reduce oxidative stress, further supporting immune function.
Incorporating Strawberries into Your Diet
Now that we’ve explored the nutritional benefits of strawberries, let’s discuss some creative ways to incorporate them into your daily diet.
Fresh and Simple
The simplest way to enjoy strawberries is fresh and unadorned. Rinse them thoroughly, remove the stems, and enjoy their sweet, juicy flavor. Fresh strawberries make a perfect snack on their own or can be added to a fruit salad for a refreshing treat.
Smoothies and Juices
Blending strawberries into smoothies or juicing them is an excellent way to reap their nutritional benefits. Combine strawberries with other fruits and vegetables, such as bananas, spinach, or kale, to create a nutrient-packed beverage. Adding a source of protein, such as yogurt or nut butter, can make your smoothie a well-rounded meal.
Salads and Savory Dishes
Strawberries add a touch of sweetness and a pop of color to savory dishes. They pair well with spinach, arugula, and other leafy greens in salads. You can also incorporate strawberries into salsa or chutney to accompany grilled meats or fish.
Baked Goods and Desserts
Strawberries are a classic ingredient in baked goods and desserts. From strawberry shortcake to strawberry rhubarb pie, the possibilities are endless. However, it’s important to remember that adding sugar and other ingredients can increase the calorie and carbohydrate content, so enjoy these treats in moderation.
Strawberry Toppings and Garnishes
Fresh strawberries can be used as a topping for yogurt, oatmeal, or pancakes. They can also be pureed and used as a natural, healthy garnish for desserts or cocktails.
Potential Allergies and Interactions
While strawberries are generally considered safe for consumption, some individuals may experience allergic reactions. Strawberry allergy is relatively rare but can cause symptoms such as hives, itching, swelling, and, in severe cases, anaphylaxis. If you suspect an allergy, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional.
Additionally, strawberries may interact with certain medications. The high vitamin C content in strawberries can interfere with the effectiveness of certain antibiotics, such as tetracyclines. It's always a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have any concerns about potential interactions.
Conclusion

Strawberries are not just a delicious treat; they are a nutritional powerhouse packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. From boosting heart health to supporting brain function and promoting skin health, strawberries offer a wide range of health benefits. By incorporating strawberries into your diet in creative and diverse ways, you can enjoy their sweet taste and reap the rewards of their nutritional prowess.
Can strawberries help with weight loss?
+Yes, strawberries can be a valuable addition to a weight loss diet. With their low-calorie content, high fiber, and nutrient density, strawberries can promote satiety and help manage weight. Additionally, the antioxidants in strawberries may aid in reducing inflammation, which is often associated with obesity and metabolic disorders.
Are frozen strawberries as nutritious as fresh ones?
+Frozen strawberries are an excellent alternative to fresh ones, especially when fresh strawberries are out of season. The freezing process helps retain most of the nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. However, some nutrients, such as vitamin C, may degrade slightly during freezing and storage.
Can strawberries be consumed by individuals with gastrointestinal issues?
+Strawberries can be a good choice for individuals with gastrointestinal issues, as they are generally well-tolerated and easy to digest. However, some people with sensitive stomachs may experience gastrointestinal symptoms, such as bloating or gas, when consuming strawberries. It’s best to introduce strawberries into the diet gradually and in small amounts to assess tolerance.