Steak Nutrition Facts Guide
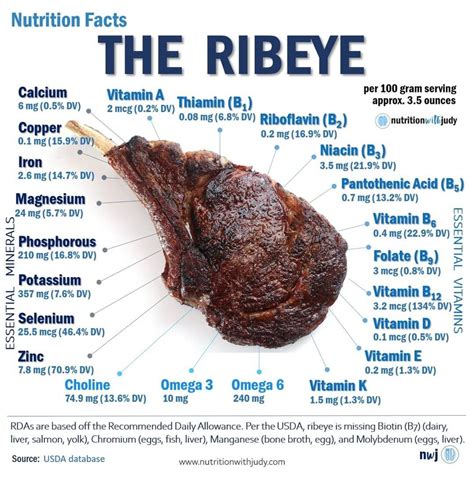
Steak, a staple in many cuisines around the world, is a nutrient-rich food that provides a significant amount of protein, vitamins, and minerals. Understanding the nutritional value of steak is essential for making informed decisions about your diet. In this guide, we will delve into the nutritional facts of steak, exploring its macronutrient composition, micronutrient content, and health implications.
Nutritional Composition of Steak

Steak is primarily composed of protein, fat, and water. The exact nutritional composition of steak varies depending on the cut, cooking method, and level of doneness. On average, a 3-ounce serving of cooked steak contains approximately 25 grams of protein, 15 grams of fat, and 0 grams of carbohydrates. The protein content of steak makes it an excellent option for individuals looking to increase their protein intake, particularly athletes and bodybuilders.
Macronutrient Breakdown
The macronutrient breakdown of steak is as follows:
| Macronutrient | Amount (per 3-ounce serving) |
|---|---|
| Protein | 25 grams |
| Fat | 15 grams |
| Carbohydrates | 0 grams |

The fat content of steak is primarily composed of saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids, with a small amount of polyunsaturated fatty acids. The fatty acid composition of steak can vary depending on the breed and diet of the cattle, as well as the cut of meat.
Micronutrient Content
Steak is a rich source of several essential micronutrients, including:
- Vitamin B12: important for the production of red blood cells and the maintenance of the nervous system
- Iron: essential for the production of hemoglobin and the transport of oxygen in the blood
- Zinc: important for immune function, wound healing, and protein synthesis
- Selenium: acts as an antioxidant in the body, protecting cells from damage and supporting immune function
Health Implications of Steak Consumption

Steak can be a part of a healthy diet when consumed in moderation. The high protein content of steak can help to support muscle growth and maintenance, while the iron and zinc content can support immune function and overall health. However, excessive consumption of steak can have negative health implications, including:
- Increased risk of heart disease due to high levels of saturated fat and cholesterol
- Increased risk of certain types of cancer, such as colorectal cancer, due to the formation of carcinogenic compounds during high-heat cooking
- Contribution to weight gain and obesity due to high calorie and fat content
- Consume steak in moderation, aiming for 1-2 servings per week
- Choose lean cuts of steak, such as sirloin or tenderloin, to minimize saturated fat intake
- Cook steak using low-heat methods, such as grilling or stir-frying, to reduce the formation of carcinogenic compounds
What is the difference between grass-fed and grain-fed beef?
+Grass-fed beef comes from cattle that are raised on a diet of grass and other forages, while grain-fed beef comes from cattle that are fed a diet of grains, such as corn and soybeans. Grass-fed beef generally contains higher levels of certain nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids and CLA, and may have a more favorable fatty acid profile.
How can I cook steak to minimize the formation of carcinogenic compounds?
+To minimize the formation of carcinogenic compounds when cooking steak, use low-heat methods, such as grilling or stir-frying, and avoid charring or burning the meat. You can also marinate the steak in a mixture containing antioxidants, such as olive oil and herbs, to help reduce the formation of carcinogenic compounds.
In conclusion, steak can be a nutritious and delicious addition to a healthy diet when consumed in moderation and prepared using low-heat methods. By understanding the nutritional composition of steak and taking steps to minimize its negative health implications, you can enjoy this popular food while supporting overall health and well-being.
