Paneer Nutrition Tips
Paneer, also known as Indian cheese, is a staple ingredient in Indian cuisine, particularly in North Indian and Pakistani dishes. It is a rich source of protein, calcium, and other essential nutrients. Paneer is made by curdling milk with lemon juice or vinegar, and then draining and pressing the curds to remove excess liquid. The nutritional profile of paneer makes it a popular choice among health-conscious individuals, but it is essential to consume it in moderation due to its high calorie and fat content.
Nutritional Profile of Paneer

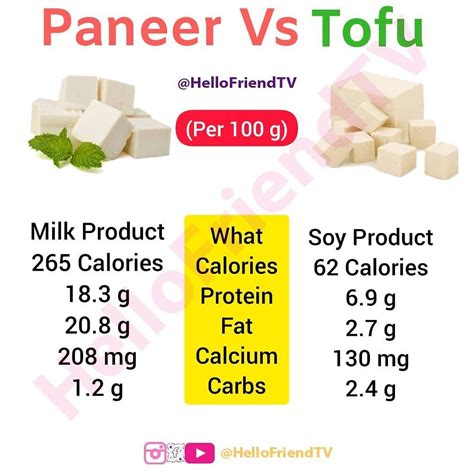
A 100-gram serving of paneer contains approximately 265 calories, 20 grams of protein, 20 grams of fat, and 1 gram of carbohydrates. It is also rich in calcium, phosphorus, and other minerals. The high protein content in paneer makes it an excellent option for vegetarians and vegans who require alternative sources of protein. Additionally, paneer is a good source of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), a fatty acid that has been linked to several health benefits, including improved immune function and body composition.
Health Benefits of Paneer
Paneer has several health benefits due to its rich nutritional profile. Some of the key benefits include:
- Strong bones and teeth: The high calcium content in paneer helps maintain strong bones and teeth, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and other bone-related disorders.
- Weight management: The high protein content in paneer helps regulate appetite and metabolism, making it an effective food for weight management.
- Improved digestion: Paneer contains probiotics, which help maintain a healthy gut microbiome and support digestion.
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases: The antioxidants and polyphenols present in paneer have been shown to reduce the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
| Nutrient | Amount (per 100g serving) |
|---|---|
| Calories | 265 |
| Protein | 20g |
| Fat | 20g |
| Carbohydrates | 1g |
| Calcium | 200mg |
| Phosphorus | 150mg |

Paneer Nutrition Tips

To get the most out of paneer, follow these nutrition tips:
- Choose low-fat paneer: Opt for low-fat or reduced-sodium paneer to minimize calorie and fat intake.
- Consume in moderation: Paneer is high in calories and fat, so it is essential to consume it in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
- Pair with nutrient-dense foods: Combine paneer with nutrient-dense foods, such as vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, to create a balanced meal.
- Avoid overcooking: Overcooking paneer can lead to a loss of nutrients, so it is essential to cook it briefly and gently.
- Experiment with different recipes: Try different recipes that incorporate paneer, such as curries, stir-fries, and salads, to add variety to your diet.
Is paneer suitable for people with lactose intolerance?
+Paneer is a low-lactose food, making it a suitable option for people with lactose intolerance. However, it is essential to note that paneer is still a dairy product and may cause issues for those with severe lactose intolerance.
Can paneer be used as a substitute for meat in a vegetarian diet?
+Yes, paneer can be used as a substitute for meat in a vegetarian diet due to its high protein content and versatility in cooking. It can be used in a variety of dishes, from curries to stir-fries, and can be marinated and grilled like meat.
In conclusion, paneer is a nutritious and versatile food that can be incorporated into a healthy diet. By following the paneer nutrition tips and choosing low-fat or reduced-sodium options, individuals can maximize the nutritional benefits of paneer while minimizing its drawbacks. Whether you are a vegetarian, vegan, or simply looking to add variety to your diet, paneer is a great option to consider.

