Nutrition Facts 1 Egg
Eggs are a nutritional powerhouse, often hailed as a complete protein source and a staple in many cuisines worldwide. The humble egg, with its versatile nature, has become a subject of fascination for nutrition enthusiasts and health-conscious individuals alike. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the nutritional facts of a single egg, uncovering its hidden benefits and exploring why it deserves a place of prominence in our daily diets.
Nutritional Composition of an Egg

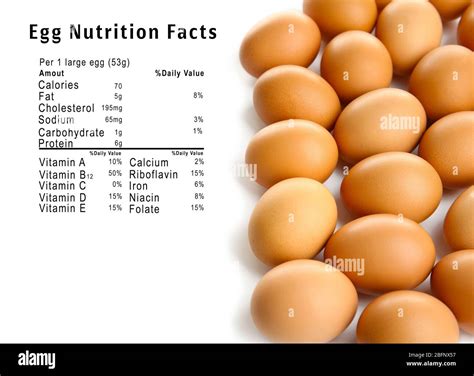
A single large egg, weighing approximately 50 grams, packs a surprising punch of nutrients. Here’s a breakdown of its nutritional profile:
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Protein | 6 grams |
| Fat | 5 grams |
| Saturated Fat | 1.5 grams |
| Cholesterol | 185 mg |
| Vitamin A | 260 IU |
| Vitamin D | 41 IU |
| Vitamin E | 0.6 mg |
| Vitamin K | 0.3 mcg |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) | 0.1 mg |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 0.2 mg |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | 0.1 mg |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | 1 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.1 mg |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.6 mcg |
| Folate | 23 mcg |
| Calcium | 26 mg |
| Iron | 0.6 mg |
| Magnesium | 6 mg |
| Phosphorus | 98 mg |
| Potassium | 68 mg |
| Sodium | 62 mg |
| Zinc | 0.5 mg |
| Copper | 0.01 mg |
| Manganese | 0.01 mg |
| Selenium | 13 mcg |

Protein Powerhouse
Eggs are renowned for their high-quality protein content. A single egg provides 6 grams of protein, which is essential for building and repairing tissues, supporting immune function, and maintaining muscle mass. The protein in eggs is considered a complete protein, containing all nine essential amino acids that our bodies cannot produce on their own.
Healthy Fats
Despite its reputation, an egg contains a modest amount of fat, with 5 grams per serving. The majority of this fat is unsaturated, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are known to have heart-healthy benefits. Eggs are also a source of omega-3 fatty acids, which are crucial for brain health and reducing inflammation.
Vitamins and Minerals
Eggs are a rich source of various vitamins and minerals. They are particularly high in vitamins A, D, and B12, which are essential for vision, bone health, and nerve function, respectively. Additionally, eggs provide a good amount of folate, a B-vitamin crucial for pregnant women and essential for fetal development.
Cholesterol Concerns
One of the most debated aspects of egg nutrition is its cholesterol content. A single egg contains 185 mg of cholesterol, which is a significant portion of the daily recommended limit. However, research has shown that dietary cholesterol from eggs has a minimal impact on blood cholesterol levels for most people. It’s important to consider individual health factors and consult with a healthcare professional when it comes to cholesterol concerns.
Health Benefits of Eggs

Beyond their nutritional composition, eggs offer a myriad of health benefits. Here are some key advantages of incorporating eggs into your diet:
Eye Health
Eggs are a great source of lutein and zeaxanthin, two powerful antioxidants that are essential for eye health. These compounds help protect the eyes from age-related macular degeneration and cataracts, reducing the risk of vision loss as we age.
Brain Function
The choline found in eggs is an essential nutrient for brain development and function. Choline plays a crucial role in memory, mood, and cognitive performance. Adequate choline intake is particularly important during pregnancy and early childhood for optimal brain development.
Weight Management
Eggs can be a valuable asset in weight management. The high protein content of eggs promotes satiety, keeping you feeling fuller for longer. This can lead to reduced calorie intake and better appetite control. Additionally, the healthy fats in eggs can help regulate blood sugar levels, preventing energy crashes and cravings.
Heart Health
Contrary to popular belief, moderate egg consumption has been linked to improved heart health. The unsaturated fats and omega-3 fatty acids in eggs can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease by lowering bad cholesterol (LDL) and increasing good cholesterol (HDL) levels.
Egg Cooking Methods and Tips
Eggs are incredibly versatile and can be prepared in a variety of ways. Here are some popular cooking methods and tips to make the most of your eggs:
Boiled Eggs
Boiling eggs is a simple and convenient way to prepare them. For a perfectly boiled egg, place the eggs in a single layer in a saucepan and cover them with cold water. Bring the water to a gentle boil, then turn off the heat and let the eggs sit for 10-12 minutes for a medium-hard boiled egg. For a softer yolk, reduce the cooking time.
Scrambled Eggs
Scrambled eggs are a breakfast favorite. Beat the eggs with a fork until well combined, then heat a non-stick pan over medium heat. Add a knob of butter or a drizzle of oil and pour in the eggs. Cook, stirring occasionally, until the eggs are cooked to your desired doneness. Season with salt and pepper to taste.
Omelets
Omelets are a versatile dish that can be customized with various fillings. Follow the same process as scrambled eggs, but once the eggs are almost set, add your desired fillings (such as cheese, vegetables, or meat) to one side of the pan. Fold the eggs over the fillings and cook for a few more minutes until the omelet is golden brown.
Poached Eggs
Poached eggs are a delicate and healthy option. Bring a saucepan of water to a gentle simmer, then crack an egg into a small bowl or cup. Create a gentle whirlpool in the water with a spoon, then carefully slip the egg into the center. Cook for 3-4 minutes for a runny yolk or longer for a firmer yolk. Lift the egg out with a slotted spoon and enjoy it on top of toast or a bed of greens.
Conclusion
The humble egg is a nutritional powerhouse, offering a wide range of health benefits and culinary versatility. From its high-quality protein and healthy fats to its rich vitamin and mineral content, the egg is a true superfood. By incorporating eggs into your diet, you can enjoy a nutritious and delicious addition to your meals, supporting your overall health and well-being.
Are eggs suitable for a vegetarian diet?
+Eggs are generally considered suitable for ovo-vegetarian diets, which allow for the consumption of eggs but not meat or dairy. However, it’s important to note that some vegetarians may have personal preferences or ethical concerns regarding egg consumption.
How many eggs can I eat per week?
+The recommended intake of eggs can vary depending on individual health factors and dietary preferences. In general, healthy adults can safely consume up to 7 eggs per week without significantly impacting cholesterol levels. However, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Can eggs help with weight loss?
+Yes, eggs can be a valuable asset in a weight loss journey. The high protein content of eggs promotes satiety, helping you feel fuller for longer and reducing overall calorie intake. Additionally, the healthy fats in eggs can help regulate blood sugar levels, preventing energy crashes and cravings.
