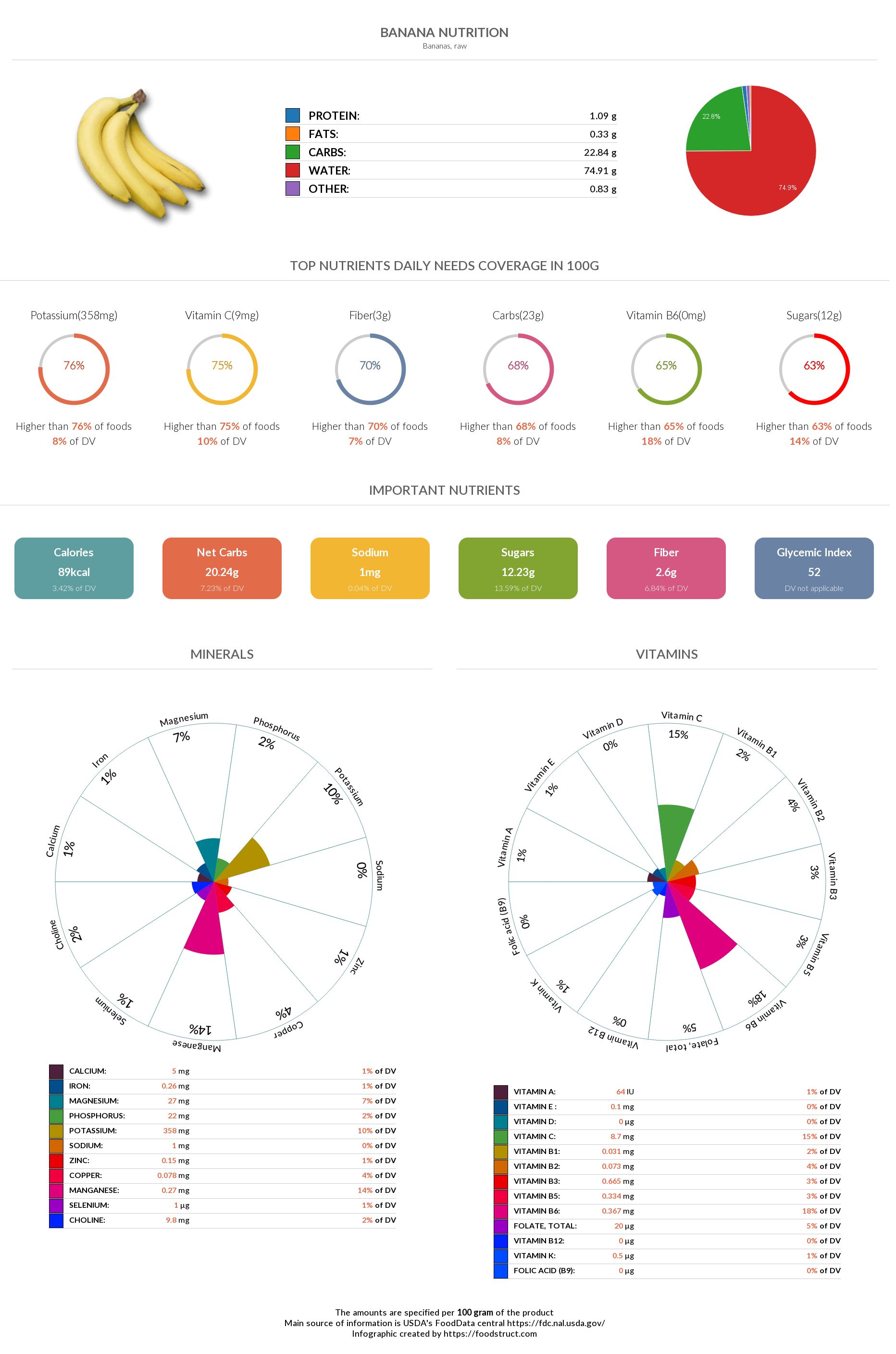
Mahi Mahi Complete Nutrition
Mahi Mahi, also known as Dolphinfish, is a tropical species of fish that is widely consumed for its rich nutritional profile and delicious flavor. Native to the warm waters of the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans, Mahi Mahi is a popular choice among seafood enthusiasts and health-conscious individuals alike. With its firm texture and rich, buttery flavor, Mahi Mahi is not only a culinary delight but also a nutrient-dense food that provides a range of essential vitamins, minerals, and proteins.
Nutritional Profile of Mahi Mahi
Mahi Mahi is an excellent source of protein, with a single 3-ounce serving providing approximately 20 grams of protein. This makes it an ideal choice for individuals looking to increase their protein intake, particularly athletes and bodybuilders. Additionally, Mahi Mahi is low in saturated fat and calories, with a 3-ounce serving containing only 1 gram of saturated fat and 120 calories. The fish is also rich in omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), which are essential for heart health and brain function.
Vitamins and Minerals in Mahi Mahi
Mahi Mahi is a rich source of various vitamins and minerals, including vitamin B12, vitamin B6, and niacin. These vitamins play a crucial role in energy metabolism, nerve function, and the formation of red blood cells. The fish is also a good source of minerals such as potassium, selenium, and phosphorus, which are essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure, immune function, and bone health.
| Nutrient | Amount per 3-ounce serving |
|---|---|
| Protein | 20 grams |
| Calories | 120 |
| Saturated Fat | 1 gram |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | 0.5 grams |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.5 micrograms |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.5 milligrams |
| Niacin | 10 milligrams |
| Potassium | 400 milligrams |
| Selenium | 45 micrograms |
| Phosphorus | 200 milligrams |
Health Benefits of Mahi Mahi
The nutritional profile of Mahi Mahi makes it an excellent addition to a healthy diet. The fish has been shown to have numerous health benefits, including reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. The omega-3 fatty acids present in Mahi Mahi have also been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as arthritis and Alzheimer’s disease.
Cooking and Preparation Methods
Mahi Mahi can be prepared in a variety of ways, including grilling, baking, and sauteing. The fish is also a popular choice for sushi and sashimi, and can be consumed raw or cooked. When cooking Mahi Mahi, it is essential to use low-heat methods to prevent the loss of nutrients and to avoid overcooking, which can make the fish dry and tough.
- Grilling: Preheat the grill to medium heat and cook the Mahi Mahi for 4-6 minutes per side, or until it reaches an internal temperature of 145°F.
- Baking: Preheat the oven to 400°F and bake the Mahi Mahi for 12-15 minutes, or until it reaches an internal temperature of 145°F.
- Sauteing: Heat a skillet over medium heat and cook the Mahi Mahi for 3-4 minutes per side, or until it reaches an internal temperature of 145°F.
Is Mahi Mahi a sustainable seafood choice?
+Mahi Mahi is a relatively sustainable seafood choice, with many fisheries and farms using responsible and eco-friendly practices. However, it is essential to choose Mahi Mahi that has been certified by organizations such as the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) or the Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC) to ensure that it has been sourced responsibly.
Can I consume Mahi Mahi if I have a shellfish allergy?
+Mahi Mahi is a finfish and is not a shellfish, so it is generally safe for individuals with shellfish allergies to consume. However, it is essential to note that Mahi Mahi may be processed in facilities that also handle shellfish, which can increase the risk of cross-contamination. If you have a shellfish allergy, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before consuming Mahi Mahi.
In conclusion, Mahi Mahi is a nutrient-dense food that provides a range of essential vitamins, minerals, and proteins. With its rich nutritional profile and delicious flavor, Mahi Mahi is an excellent addition to a healthy diet. Whether grilled, baked, or sauteed, Mahi Mahi is a versatile and sustainable seafood choice that can be enjoyed by individuals of all ages and dietary backgrounds.