Cooked White Rice: A Comprehensive Nutrition Breakdown For Health

White rice, a staple food for billions worldwide, is often the subject of debate when it comes to its nutritional value. While it is a versatile and widely consumed food, there are misconceptions about its nutritional content and potential health benefits. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of cooked white rice, exploring its nutritional breakdown, the impact of processing, and its role in a balanced diet.
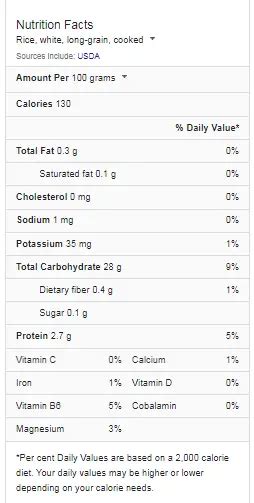
Nutritional Profile of Cooked White Rice

White rice, scientifically known as Oryza sativa, undergoes a milling process that removes the outer bran and germ layers, resulting in a refined grain. This processing step significantly alters its nutritional composition compared to its whole-grain counterpart, brown rice. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the key nutrients found in cooked white rice:
Carbohydrates and Energy
White rice is primarily composed of carbohydrates, providing a quick and readily available source of energy. A 100-gram serving of cooked white rice contains approximately:
- 87.69 grams of Carbohydrates, making it an excellent energy source for active individuals.
- 132 Calories, offering a moderate energy boost.
Protein and Amino Acids
While white rice is not a significant source of protein, it does contribute to our daily protein intake. A 100-gram serving contains:
- 2.61 grams of Protein, including essential amino acids like lysine and methionine.
Vitamins and Minerals
Cooked white rice contains various vitamins and minerals, although in smaller quantities compared to whole grains. Here’s a snapshot of its vitamin and mineral content:
| Vitamin/Mineral | Amount (per 100g) |
|---|---|
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) | 0.06 mg |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 0.02 mg |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | 1.25 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.08 mg |
| Vitamin B9 (Folate) | 11 µg |
| Calcium | 2 mg |
| Iron | 0.62 mg |
| Magnesium | 16 mg |
| Phosphorus | 56 mg |
| Potassium | 36 mg |

Dietary Fiber
The milling process reduces the fiber content of white rice. A 100-gram serving contains:
- 0.3 grams of Dietary Fiber, which is significantly lower than whole grains.
The Impact of Processing on White Rice

The refining process that transforms brown rice into white rice has both advantages and drawbacks. While it extends the rice’s shelf life and improves its texture, it also strips away essential nutrients. Here’s a closer look at the impact of processing:
Nutrient Loss
During the milling process, white rice loses a significant portion of its vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. This nutrient depletion can be a concern, especially for individuals with limited access to a diverse diet.
Enriched Rice
To mitigate the nutrient loss, many countries fortify white rice with essential vitamins and minerals. This process, known as enrichment, aims to restore some of the nutrients lost during milling. Enriched white rice often contains added iron, folic acid, and vitamins B1, B3, and B6.
Glycemic Index
White rice has a higher glycemic index (GI) compared to brown rice. This means it can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, which may be a concern for individuals with diabetes or those aiming to manage their blood sugar levels.
White Rice in a Balanced Diet
Despite its refined nature, white rice can still be a part of a healthy and balanced diet. Here’s how to incorporate it mindfully:
Portion Control
Given its high carbohydrate content, it’s essential to practice portion control. Aim for moderate servings to ensure a balanced intake of nutrients.
Combine with Other Foods
Pairing white rice with nutrient-dense foods can enhance its nutritional value. Combine it with lean proteins, vegetables, and healthy fats to create a well-rounded meal.
Opt for Brown Rice
When possible, consider choosing brown rice over white rice. Brown rice retains its nutrient-rich bran and germ layers, offering a higher nutritional profile.
Fortified Options
If white rice is a staple in your diet, opt for fortified varieties to ensure you’re getting essential nutrients.
Health Benefits of White Rice
While white rice may not be as nutrient-dense as whole grains, it still offers some health benefits:
Easy to Digest
White rice is gentle on the digestive system and can be a suitable option for individuals with digestive issues or those recovering from illness.
Gluten-Free
White rice is naturally gluten-free, making it a safe choice for individuals with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease.
Energy Boost
The high carbohydrate content provides a quick energy boost, making it an ideal pre-workout or post-workout meal.
Culinary Uses and Recipes
White rice is a versatile ingredient in the kitchen, lending itself to a variety of dishes. Here are some popular ways to enjoy white rice:
Classic Rice Bowl
Combine cooked white rice with your choice of protein (chicken, tofu, or shrimp), vegetables (carrots, bell peppers, and onions), and a flavorful sauce (teriyaki or peanut). Top it off with a sprinkle of sesame seeds for a delicious and nutritious meal.
Rice Pudding
For a sweet treat, try making rice pudding. Cook white rice with milk, cinnamon, and a touch of vanilla. Serve it warm or chilled, and top it with your favorite fruits for a satisfying dessert.
Fried Rice
Fried rice is a popular dish worldwide. Sauté cooked white rice with vegetables, eggs, and your choice of protein. Season it with soy sauce, ginger, and garlic for a flavorful and filling meal.
Conclusion
Cooked white rice, when consumed in moderation and as part of a diverse diet, can be a valuable addition to your nutritional regimen. While it may not offer the same nutritional benefits as whole grains, its versatility and ease of digestion make it a popular choice for many. By understanding its nutritional profile and making informed choices, you can enjoy white rice as a delicious and nutritious part of your meals.
Is white rice healthy for weight loss?
+White rice can be included in a weight loss diet when consumed in moderation. Its high carbohydrate content provides energy, but portion control is key. Combining it with lean proteins and vegetables can create a satisfying and nutrient-rich meal.
Can white rice cause blood sugar spikes?
+Yes, white rice has a higher glycemic index, which can lead to blood sugar spikes. Individuals with diabetes or those managing blood sugar levels should be mindful of their intake and consider pairing it with low-GI foods.
Is white rice suitable for a gluten-free diet?
+Absolutely! White rice is naturally gluten-free, making it a safe choice for individuals with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease. It can be a staple in gluten-free diets, providing a source of energy and carbohydrates.
