12 Kale Nutrients: Unlocking Its Nutritional Power
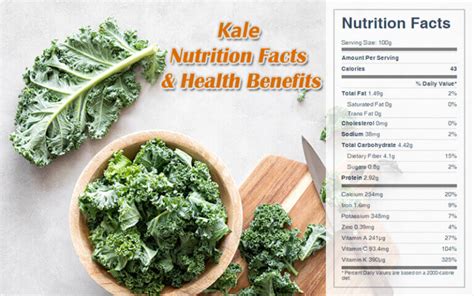
Kale, a leafy green vegetable, has gained immense popularity in recent years for its exceptional nutritional value. With a wide array of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, kale has become a staple in health-conscious diets. In this article, we will delve into the 12 key nutrients found in kale and explore how they contribute to its nutritional prowess.
The Nutritional Powerhouse: Kale’s 12 Key Nutrients

Kale, scientifically known as Brassica oleracea, is a cruciferous vegetable that has been cultivated for centuries. Its nutrient density sets it apart from many other foods, making it a valuable addition to any diet. Let’s uncover the nutritional treasures hidden within this vibrant green vegetable.
1. Vitamin K: The Bone Health Booster
Kale is an exceptional source of vitamin K, a fat-soluble vitamin essential for bone health. Vitamin K plays a crucial role in calcium absorption and bone mineralization. A single cup of kale provides a staggering 684% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin K, making it an excellent choice for maintaining strong and healthy bones.
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 cup (67g) |
|---|---|
| Vitamin K | 547.4 mcg (684% DV) |

2. Vitamin C: Immune System Support
Kale is packed with vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant that strengthens the immune system. Vitamin C aids in the production of white blood cells, enhances iron absorption, and supports collagen formation. A cup of kale provides approximately 134% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin C, making it an excellent natural source of this vital nutrient.
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 cup (67g) |
|---|---|
| Vitamin C | 80.4 mg (134% DV) |
3. Calcium: Building Strong Bones and Teeth
Kale is an excellent plant-based source of calcium, a mineral crucial for bone health and overall bodily functions. Calcium is essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth, as well as supporting muscle function and nerve transmission. A cup of kale contains a notable 9% of the recommended daily intake of calcium, making it a valuable addition to a calcium-rich diet.
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 cup (67g) |
|---|---|
| Calcium | 121.5 mg (9% DV) |
4. Iron: Essential for Oxygen Transport
Kale is a good source of iron, a mineral that plays a vital role in oxygen transport throughout the body. Iron is necessary for the production of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. A cup of kale provides approximately 6% of the recommended daily intake of iron, contributing to overall health and energy levels.
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 cup (67g) |
|---|---|
| Iron | 1.1 mg (6% DV) |
5. Vitamin A: Vision and Immune Health
Kale is rich in vitamin A, a fat-soluble vitamin essential for vision, immune function, and cellular growth. Vitamin A supports healthy vision by maintaining the retina and promoting the production of rhodopsin, a protein necessary for low-light vision. Additionally, it strengthens the immune system and helps fight infections. A cup of kale provides a substantial 206% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin A, making it an excellent natural source.
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 cup (67g) |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 444 mcg RAE (206% DV) |
6. Vitamin B6: Brain and Nerve Function
Kale contains vitamin B6, a water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in brain and nerve function. Vitamin B6 is involved in the production of neurotransmitters, which are essential for communication between nerve cells. It also helps convert food into energy and supports the formation of red blood cells. A cup of kale provides approximately 11% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin B6, contributing to overall brain health.
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 cup (67g) |
|---|---|
| Vitamin B6 | 0.1 mg (11% DV) |
7. Magnesium: Muscle and Nerve Function
Kale is a good source of magnesium, a mineral that plays a vital role in muscle and nerve function. Magnesium is involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, including muscle contraction, nerve transmission, and energy production. A cup of kale provides approximately 6% of the recommended daily intake of magnesium, supporting overall muscle and nerve health.
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 cup (67g) |
|---|---|
| Magnesium | 15.3 mg (6% DV) |
8. Potassium: Heart Health and Blood Pressure
Kale is rich in potassium, an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in heart health and blood pressure regulation. Potassium helps maintain a healthy balance of fluids in the body and supports proper muscle and nerve function. It also works to counteract the effects of sodium, helping to lower blood pressure. A cup of kale provides approximately 9% of the recommended daily intake of potassium, making it a heart-healthy choice.
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 cup (67g) |
|---|---|
| Potassium | 299 mg (9% DV) |
9. Folate: DNA Synthesis and Cell Division
Kale is an excellent source of folate, a water-soluble B vitamin that plays a crucial role in DNA synthesis and cell division. Folate is particularly important during periods of rapid growth, such as pregnancy and infancy. It helps prevent neural tube defects in developing fetuses and supports overall cellular health. A cup of kale provides approximately 18% of the recommended daily intake of folate, making it a valuable addition to a folate-rich diet.
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 cup (67g) |
|---|---|
| Folate | 53.2 mcg (18% DV) |
10. Vitamin E: Antioxidant Power
Kale contains vitamin E, a fat-soluble vitamin with powerful antioxidant properties. Vitamin E helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can contribute to chronic diseases. It also supports a healthy immune system and may have anti-inflammatory effects. A cup of kale provides approximately 5% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin E, contributing to overall antioxidant defense.
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 cup (67g) |
|---|---|
| Vitamin E | 1.1 mg (5% DV) |
11. Manganese: Enzyme Function and Bone Health
Kale is a good source of manganese, a trace mineral that plays a vital role in enzyme function and bone health. Manganese is involved in the activation of enzymes that are essential for various biochemical reactions in the body. It also contributes to bone development and maintenance, working alongside other minerals like calcium and zinc. A cup of kale provides approximately 16% of the recommended daily intake of manganese, supporting overall bone health.
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 cup (67g) |
|---|---|
| Manganese | 0.5 mg (16% DV) |
12. Fiber: Digestive Health and Satiety
Kale is a fiber-rich vegetable, providing both soluble and insoluble fiber. Fiber is essential for digestive health, as it promotes regular bowel movements and helps prevent constipation. It also contributes to a feeling of fullness, aiding in weight management. A cup of kale contains approximately 2.5 grams of fiber, making it a valuable source of this essential nutrient.
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 cup (67g) |
|---|---|
| Fiber | 2.5 g |
Conclusion: Embracing Kale’s Nutritional Benefits

Kale, with its impressive array of nutrients, is truly a nutritional powerhouse. From supporting bone health and boosting the immune system to aiding in digestion and providing essential minerals, kale offers a wide range of health benefits. By incorporating kale into your diet, you can unlock its nutritional power and take a step towards a healthier and more vibrant life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can kale be consumed raw or cooked?
+Kale can be enjoyed both raw and cooked. Raw kale has a crisp and slightly bitter taste, making it a popular addition to salads and smoothies. Cooking kale, such as steaming or sautéing, softens its texture and reduces bitterness, making it more palatable for some individuals. Both raw and cooked kale offer nutritional benefits, so choose the preparation method that suits your taste preferences.
Is kale suitable for individuals with thyroid issues?
+Kale, like other cruciferous vegetables, contains goitrogens, which can interfere with thyroid function in large amounts. However, moderate consumption of kale is generally considered safe for individuals with thyroid issues. Cooking kale can help reduce the goitrogenic compounds, making it a suitable option for those with thyroid concerns. As always, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
How can I incorporate more kale into my diet?
+There are numerous ways to incorporate kale into your diet. You can add raw kale to salads or smoothies, blend it into green juices, or use it as a base for soups and stews. Sautéed kale makes a delicious side dish, and you can also use kale in place of lettuce in sandwiches or wraps. Get creative with kale chips, kale pesto, or even kale-infused smoothies for a nutritious and flavorful boost.