11 Egg Nutrition Facts You Should Know
Eggs, a versatile and widely consumed food, have long been a subject of interest and debate among nutritionists, health enthusiasts, and the general public. With a reputation for being a nutritional powerhouse, eggs offer a wide range of benefits, but they also come with certain considerations. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into 11 essential egg nutrition facts, backed by scientific evidence, to help you make informed choices about incorporating this popular food into your diet.
1. Nutritional Composition of Eggs

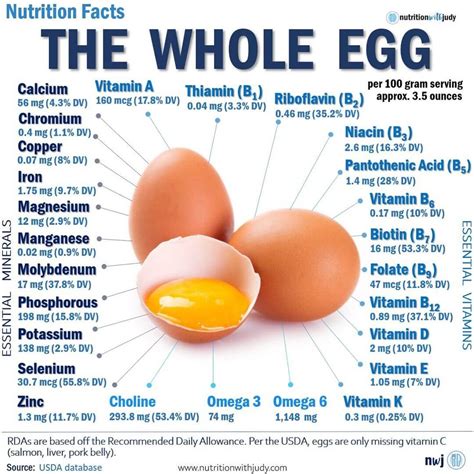
A single large egg, weighing approximately 50 grams, is a nutrient-dense package. It contains high-quality protein, essential amino acids, healthy fats, and a host of vitamins and minerals. Here’s a breakdown of the key nutrients found in eggs:
- Protein: Eggs are an excellent source of complete protein, providing all the essential amino acids required by the body. A large egg contains around 6 grams of protein, making it a valuable addition to a balanced diet.
- Healthy Fats: While eggs have a reputation for being high in cholesterol, they also contain beneficial fats. Approximately 5 grams of fat are present in a large egg, including omega-3 fatty acids, which are crucial for brain health and reducing inflammation.
- Vitamins: Eggs are rich in various vitamins, including vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin E, and vitamin B12. These vitamins play vital roles in maintaining eye health, supporting immune function, and promoting overall well-being.
- Minerals: Essential minerals like iron, phosphorus, and selenium are found in eggs. Iron is crucial for oxygen transport in the body, while phosphorus supports bone health, and selenium acts as an antioxidant.
2. The Cholesterol Debate

One of the most controversial aspects of egg nutrition is its cholesterol content. A large egg contains around 186 mg of cholesterol, which is about 62% of the recommended daily intake. This has led to concerns about the impact of egg consumption on heart health.
However, recent research suggests that dietary cholesterol from eggs may not have as significant an impact on blood cholesterol levels as previously believed. Studies have shown that eating eggs in moderation does not increase the risk of heart disease for most people. In fact, the high-quality protein and essential nutrients in eggs can contribute to a healthy diet.
Moderation and Individual Considerations
While eggs can be a part of a healthy diet, moderation is key. The American Heart Association recommends limiting cholesterol intake to less than 300 mg per day. For individuals with high cholesterol or heart disease, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to determine an appropriate egg intake.
3. The Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Eggs are a natural source of omega-3 fatty acids, which are known for their numerous health benefits. These essential fatty acids cannot be produced by the body and must be obtained through diet.
Omega-3 fatty acids have been linked to improved heart health, reduced inflammation, and better brain function. They may also play a role in reducing the risk of certain chronic diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and arthritis.
Enhancing Omega-3 Content
The omega-3 content of eggs can be enhanced by feeding chickens a diet rich in omega-3-containing foods like flaxseed or fish oil. These “omega-3-enriched” eggs can provide an even greater source of these beneficial fatty acids.
4. Egg Quality and Nutrition
The nutritional value of eggs can vary depending on factors such as the hen’s diet, breed, and living conditions. Here’s a breakdown of the different types of eggs and their nutritional profiles:
- Cage-Free Eggs: These eggs come from hens that are not confined to cages but may still be housed indoors. They tend to have slightly higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E compared to conventional eggs.
- Free-Range Eggs: Hens producing free-range eggs have access to the outdoors and may forage for natural foods. These eggs often have higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin A.
- Organic Eggs: Organic eggs come from hens that are fed an organic, vegetarian diet free from pesticides and antibiotics. They may have slightly higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E.
- Pasture-Raised Eggs: Pasture-raised hens have the most natural and diverse diet, as they forage for insects, grasses, and seeds. These eggs typically have the highest levels of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin A, and other nutrients.
5. Egg Protein and Muscle Health
The high-quality protein in eggs makes them an excellent choice for supporting muscle health and recovery. Egg protein contains all the essential amino acids needed for muscle growth and repair.
Research has shown that consuming eggs post-workout can promote muscle protein synthesis and help repair and rebuild muscle tissue. This makes eggs a valuable addition to the diet of athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
Ideal Post-Workout Meal
Combining eggs with other protein-rich foods, such as lean meats or dairy products, can further enhance muscle recovery and growth. A post-workout meal might include scrambled eggs with vegetables and a side of lean protein.
6. Eggs and Weight Management
Despite their high nutritional value, eggs are often overlooked as a weight-loss-friendly food. However, research suggests that incorporating eggs into a calorie-controlled diet can be beneficial for weight management.
Eggs are satiating, meaning they promote a feeling of fullness and can help reduce overall calorie intake. Additionally, the high-quality protein in eggs can boost metabolism and support lean muscle mass, both of which are important for weight loss and maintenance.
Egg-Based Meal Ideas
Incorporating eggs into your diet can be as simple as having a boiled egg as a snack or adding an egg to your salad. Here are a few egg-based meal ideas for weight management:
- Egg white omelet with vegetables
- Poached eggs on whole-grain toast with avocado
- Hard-boiled egg and vegetable frittata
7. Eggs and Eye Health
Eggs are a rich source of two essential nutrients for eye health: lutein and zeaxanthin. These carotenoids are found in the yolk and are known for their ability to reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.
Research has shown that consuming eggs regularly can increase the levels of lutein and zeaxanthin in the blood, which may help protect against eye diseases and maintain overall eye health.
Eye-Healthy Diet
In addition to eggs, incorporating other lutein- and zeaxanthin-rich foods into your diet can further support eye health. These include leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and kale, as well as orange and yellow fruits and vegetables like carrots and sweet potatoes.
8. Eggs and Brain Health
The nutrients found in eggs, including choline, omega-3 fatty acids, and B vitamins, play a crucial role in brain health and cognitive function.
Choline, in particular, is essential for brain development and memory function. It is also involved in the production of neurotransmitters, which are crucial for communication between brain cells.
Brain-Boosting Egg Recipes
Incorporating eggs into your diet can be a delicious way to support brain health. Here are a few egg-based recipes to try:
- Egg and avocado toast with a sprinkle of chives
- Smoked salmon and egg breakfast bowl
- Baked eggs with spinach and feta
9. Eggs and Immune Function
Eggs are a good source of selenium, a mineral that plays a vital role in immune function. Selenium is involved in the production of antibodies and helps regulate the immune response.
Additionally, the vitamin A and vitamin E found in eggs contribute to a healthy immune system by supporting the function of immune cells and protecting against oxidative stress.
Immune-Boosting Foods
To further support immune function, consider incorporating other immune-boosting foods into your diet. These include citrus fruits for vitamin C, garlic and ginger for their antimicrobial properties, and yogurt for its beneficial probiotics.
10. Egg Safety and Storage
While eggs are a nutritious food, it’s important to handle and store them properly to ensure food safety. Here are some key tips for egg safety and storage:
- Check the expiration date on the egg carton and avoid using eggs that are past their prime.
- Store eggs in their original carton in the coldest part of the refrigerator, ideally in the back of the fridge where the temperature is most consistent.
- Avoid washing eggs before storing them, as this can remove the natural protective coating on the shell.
- If you crack an egg and notice an off odor or unusual appearance, discard it immediately.
11. Egg Allergies and Sensitivities
Despite their nutritional benefits, eggs can cause allergic reactions in some individuals. Egg allergies are one of the most common food allergies, particularly in children.
Symptoms of an egg allergy can range from mild, such as hives or itching, to severe, including anaphylaxis. If you suspect an egg allergy, it’s important to consult with an allergist for proper testing and guidance.
Egg Alternatives
For those with egg allergies or dietary preferences that exclude eggs, there are several egg alternatives available. These include:
- Flaxseed or chia seed meal
- Baking powder and water mixture
- Silken tofu
- Commercial egg replacers
Conclusion
Eggs are a versatile and nutritious food that can be a valuable addition to a healthy diet. From their high-quality protein and essential nutrients to their potential health benefits, eggs offer a range of advantages. However, it’s important to consider individual needs and dietary preferences when incorporating eggs into your diet.
By understanding the nutritional composition of eggs and their potential impacts on health, you can make informed choices about including this popular food in your meals. Whether you’re an athlete looking to support muscle recovery or an individual aiming for a balanced diet, eggs can be a delicious and nutritious part of your culinary journey.
How many eggs can I safely eat per week?
+The recommended weekly egg intake varies depending on individual health and dietary goals. For most healthy adults, consuming up to 7 eggs per week is considered safe and can be part of a balanced diet. However, for individuals with high cholesterol or heart disease, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to determine an appropriate egg intake.
Are egg whites healthier than egg yolks?
+While egg whites are a good source of protein and low in fat, egg yolks contain essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats. Eating the whole egg ensures you get the full range of nutrients. However, if you’re watching your cholesterol intake, you may opt for egg whites or consult with a healthcare professional for guidance.
Can eggs help with weight loss?
+Yes, eggs can be a valuable addition to a weight-loss diet. They are satiating, meaning they promote a feeling of fullness, and their high-quality protein can help boost metabolism. Incorporating eggs into a calorie-controlled diet can support weight loss and maintenance.