11 Broccoli Nutrition Facts: A Healthy Cup
Broccoli, a cruciferous vegetable, is a nutritional powerhouse that has been a staple in many cuisines around the world. With its distinctive tree-like structure and vibrant green color, broccoli not only adds a pop of color to your plate but also packs a punch of essential nutrients. In this article, we will dive into the nutritional profile of broccoli, exploring its remarkable health benefits and the science behind them.
The Nutritional Profile of Broccoli

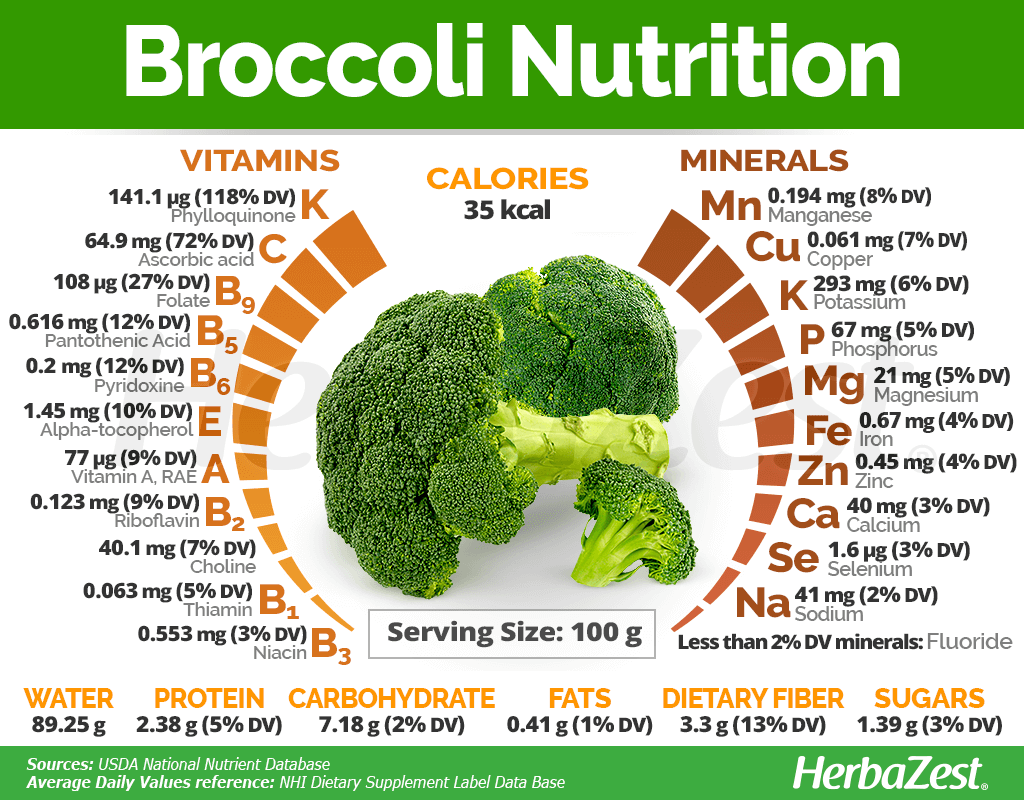
A single cup of raw broccoli, weighing approximately 91 grams, is a nutritional treasure trove. Here’s a breakdown of the key nutrients you can expect to find in this healthy serving:
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calories | 31 |
| Protein | 2.6 grams |
| Fiber | 2.4 grams |
| Vitamin C | 132% of the Reference Daily Intake (RDI) |
| Vitamin K | 144% of the RDI |
| Folate (Vitamin B9) | 14% of the RDI |
| Potassium | 5% of the RDI |
| Manganese | 8% of the RDI |
| Vitamin A | 11% of the RDI |
| Iron | 4% of the RDI |
| Magnesium | 4% of the RDI |

Broccoli's nutritional composition is impressive, offering a wide array of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Its low-calorie content, coupled with a high fiber and protein content, makes it an excellent choice for those aiming to maintain a healthy weight or manage their blood sugar levels.
Health Benefits of Broccoli

The health benefits of broccoli are vast and well-documented. Here are some of the key advantages that make this vegetable a must-have in your diet:
1. Rich in Antioxidants
Broccoli is a powerhouse of antioxidants, including flavonoids, carotenoids, and vitamin C. These antioxidants help combat oxidative stress in the body, reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and certain types of cancer. Broccoli’s high vitamin C content also supports immune function and aids in the absorption of non-heme iron from plant-based foods.
2. Supports Heart Health
The fiber and potassium content in broccoli contribute to heart health. Fiber helps lower cholesterol levels, while potassium plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy blood pressure. Additionally, broccoli contains glucosinolates, which are compounds that have been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease.
3. Promotes Digestive Health
With its high fiber content, broccoli supports a healthy digestive system. Fiber adds bulk to the stool, promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Furthermore, broccoli contains prebiotics, which serve as food for beneficial gut bacteria, fostering a healthy gut microbiome.
4. May Reduce Cancer Risk
Research suggests that broccoli’s glucosinolates and other compounds may have cancer-fighting properties. These compounds can help detoxify and eliminate potential carcinogens from the body, potentially reducing the risk of certain cancers, including colorectal, breast, and prostate cancer.
5. Supports Bone Health
Broccoli is a good source of vitamin K, which plays a vital role in bone health. Vitamin K helps improve calcium absorption and reduces its excretion, thereby promoting bone density and strength. Additionally, broccoli contains other bone-friendly nutrients like vitamin C, which is essential for collagen production, and manganese, which supports bone mineralization.
6. May Improve Brain Function
The antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds in broccoli may have neuroprotective effects. These compounds can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, potentially improving cognitive function and reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
7. Aids in Weight Management
With its low-calorie and high-fiber content, broccoli can be a valuable addition to a weight-loss or weight-maintenance diet. The fiber in broccoli promotes a feeling of fullness, helping to control appetite and reduce overall calorie intake. Additionally, broccoli’s low energy density means you can eat a substantial volume of this vegetable without consuming excessive calories.
Incorporating Broccoli into Your Diet
Broccoli is incredibly versatile and can be prepared in a variety of ways to suit different tastes and dietary preferences. Here are some ideas to help you incorporate more broccoli into your meals:
- Steam or roast broccoli as a side dish.
- Add chopped broccoli to stir-fries, soups, or casseroles.
- Toss broccoli florets with olive oil and your favorite spices, then roast them in the oven for a delicious and healthy snack.
- Blend broccoli into smoothies for a nutritional boost.
- Make broccoli the star of the show by creating a broccoli-based dish, such as a broccoli frittata or broccoli soup.
When preparing broccoli, it's best to cook it lightly to preserve its nutritional content. Overcooking can lead to a loss of vitamins and minerals. Steaming or roasting are excellent cooking methods that retain broccoli's nutritional value.
Potential Considerations
While broccoli is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience digestive issues such as gas or bloating when consuming it. This is often due to the high fiber content and can be mitigated by gradually increasing your broccoli intake and ensuring adequate hydration.
Additionally, broccoli is a member of the cruciferous vegetable family, which also includes cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage. If you have a known allergy or sensitivity to these vegetables, it's best to avoid broccoli or consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating it into your diet.
Conclusion

Broccoli is a nutritional powerhouse that offers a wide range of health benefits. Its impressive nutrient profile, including antioxidants, fiber, and vitamins, makes it an excellent addition to a healthy diet. By incorporating broccoli into your meals, you can take advantage of its numerous health-promoting properties and support your overall well-being.
Is broccoli suitable for individuals with thyroid conditions?
+Broccoli, like other cruciferous vegetables, contains goitrogens, which can interfere with thyroid function in large amounts. However, moderate consumption of broccoli is generally safe for individuals with thyroid conditions. Cooking broccoli can also reduce the goitrogenic effect.
Can broccoli be frozen for later use?
+Yes, broccoli can be frozen to extend its shelf life. To freeze broccoli, blanch it in boiling water for a few minutes, then quickly immerse it in ice water to stop the cooking process. Drain the broccoli and store it in an airtight container or freezer bag. Frozen broccoli can be used in a variety of recipes.
What are some creative ways to serve broccoli to picky eaters?
+For picky eaters, try serving broccoli in creative ways, such as baked broccoli tots, broccoli “trees” with a dip, or blended into a creamy soup. You can also hide broccoli in dishes like pasta sauces or casseroles.

